What is Testicular and Epididymal Infection? A Serious Condition Threatening Men’s Health: Orchitis and Epididymitis
Testicular and epididymal infection is one of the most common problems affecting the male reproductive system. Generally painful and uncomfortable, this condition can be easily controlled with early diagnosis and correct treatment. However, if neglected, it can lead to serious complications, including infertility.
So, what exactly are these infections, known as Orchitis and Epididymitis, how do they occur, and what symptoms do they present?
1. What is Epididymitis (Inflammation of the Seminal Duct)?
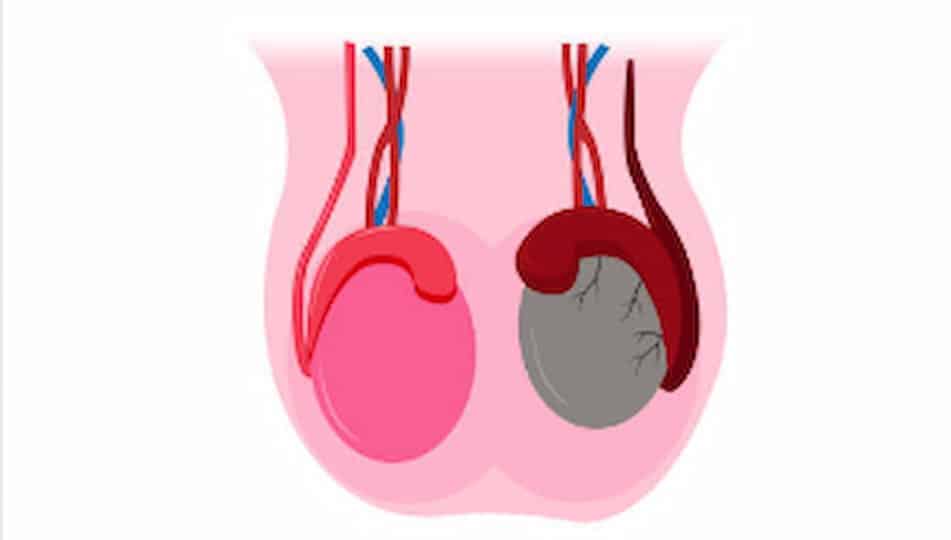
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis, the thin, coiled tube located behind the testicles that stores and transports sperm. Epididymitis is the most common type and can occur in men of all ages, but is especially prevalent in sexually active men between the ages of 14 and 35.
- Acute Epididymitis: Symptoms start suddenly and last a short time.
- Chronic Epididymitis: Symptoms last longer than 6 weeks or recur frequently.
2. What is Orchitis (Testicular Inflammation)?
Orchitis is the direct inflammation of the testicular tissue. Although Orchitis usually affects a single testicle, both testicles can rarely be involved.
What is Epididymo-orchitis?
Most of the time, the infection spreads from the epididymis to the testicle or vice versa. When both the epididymis and the testicle are inflamed, the condition is called Epididymo-orchitis, and its symptoms are generally more severe.
What Causes Testicular and Epididymal Infection?
The main cause of these infections is generally bacterial or viral agents. The source of the infection varies depending on the patient’s age and sexual activity.
A. Causes in Young and Sexually Active Men (Bacterial)
In this age group, the most common causes of infection are bacteria that cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs):
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
B. Causes in Children and Elderly Men (Bacterial and Viral)
Non-sexually transmitted causes usually arise from infections of the urinary tract or other parts of the body:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI): Bacteria advancing from the urinary tract (most commonly E. Coli) can reach the epididymis and cause inflammation.
- Mumps Virus: This can cause orchitis, especially in men who contract mumps after adolescence.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): In older age, the inability to fully empty the bladder and the backflow (reflux) of urine can create a basis for infection.
- Urinary System Interventions: Procedures such as urethral catheterization or surgery.
- Trauma: Direct blows to the groin area.
What are the Symptoms of Testicular and Epididymal Infection?
Symptoms of Epididymitis and Orchitis are similar and usually begin suddenly:
Testicular and epididymal infections are a serious condition and require prompt evaluation by a Urologist. Since sudden and severe testicular pain can be confused with conditions requiring emergency surgery, such as testicular torsion (twisting of the testicle around its axis), it is considered a medical emergency.
How is Treatment Performed?
- Antibiotic Treatment: In bacterial infections (the most common type), your doctor will start an appropriate antibiotic treatment targeting the infectious agent. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms disappear.
- Pain Relievers (NSAIDs): Prescription or over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Supportive Treatments: Rest, using scrotal support to elevate the affected testicle, and applying local cold compresses help alleviate discomfort.
- Viral Orchitis Treatment: Antibiotics are not effective in viral-caused orchitis (like mumps). Treatment focuses on symptom relief and supportive care.
Possible Complications if Not Treated
If testicular and epididymal infection is not treated correctly and timely, it can lead to the following serious problems:
- Abscess Formation: Pus-filled sacs (abscess) can form inside the testicle or epididymis, often requiring surgical drainage.
- Chronic Pain: Long-term, non-resolving testicular pain (chronic epididymitis) may develop even after the infection has passed.
- Infertility: Especially infections affecting both sides or abscess formation can cause permanent blockage in the sperm-carrying ducts, leading to male infertility.
- Loss of the Testicle (Orchiectomy): In very rare and severe cases, surgical removal of the testicle may be required due to an uncontrolled infection.
Infections of the testicle and epididymis are vital for men’s health; early diagnosis saves lives and prevents permanent problems. The moment you notice pain, swelling, or redness in the testicular area, you should immediately consult a urologist.